Flutter & Dart
Table of Contents
- 1. Flutter Basics
- 1.1. Types of Widgets
- 1.2. Button onPressed
- 1.3. Anonymous Functions
- 1.4. Dart list
- 1.5. State
- 1.6. Class and Object Visibility in Dart
- 1.7. Positional arguements and named arguements
- 1.8. Centering widget
- 1.9. Mutliple constructors
- 1.10. Dart casting (?)
- 1.11. Dart spread(?) … operator
- 1.12. Dart final vs const
- 1.13. Getters
- 2. Debugging
- 3. Widget, Styling, Logic (Building Real App)
- 3.1. Most Important Widgets
- 3.2. Combining Widgets
- 3.3. Populating List to Widgets
- 3.4. Formatting Date
- 3.5. Text Input Widget
- 3.6. Scrolling Functionality
- 3.7. Some
TextField()parameters - 3.8. Printing double values
- 3.9. Adding a button to AppBar
- 3.10. Floating Button
- 3.11. Showing a Modal Bottom Sheet
- 3.12. Reaching to a field in
StatefullWidgetfromState<> - 3.13. Automatic closing of widget when user inputs the data
- 3.14. Themeing
- 3.15. Fonts
- 3.16. Adding Image
- 3.17.
SizedBox()andFractionallySizedBox() - 3.18.
Flexible() - 3.19.
FittedBox() - 3.20.
Future<>
- 4. Responsive & Adapted User Interfaces and Apps
- 5. Widget & Flutter Internals
1 Flutter Basics
Everything is a widget in flutter.
Simple hello world application:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp(home: Text("Hello!"),); } }
Different syntax of calling functions in functions. This is equal with the code up there.
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
Instead of text, we can call Scaffold:
- Basic design scheme comes from
material.dartpackage
return MaterialApp(home: Scaffold());
- Add coma after paranthesis to format code in a more readable way.
home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('My first App'), ), // Appbar body: Text("This is my default text!"), ), // Scaffold
1.1 Types of Widgets
1.1.1 Outuput & Input (Visible)
RaisedButton()Text()Card()- …
1.1.2 Layout & Control (Invisible)
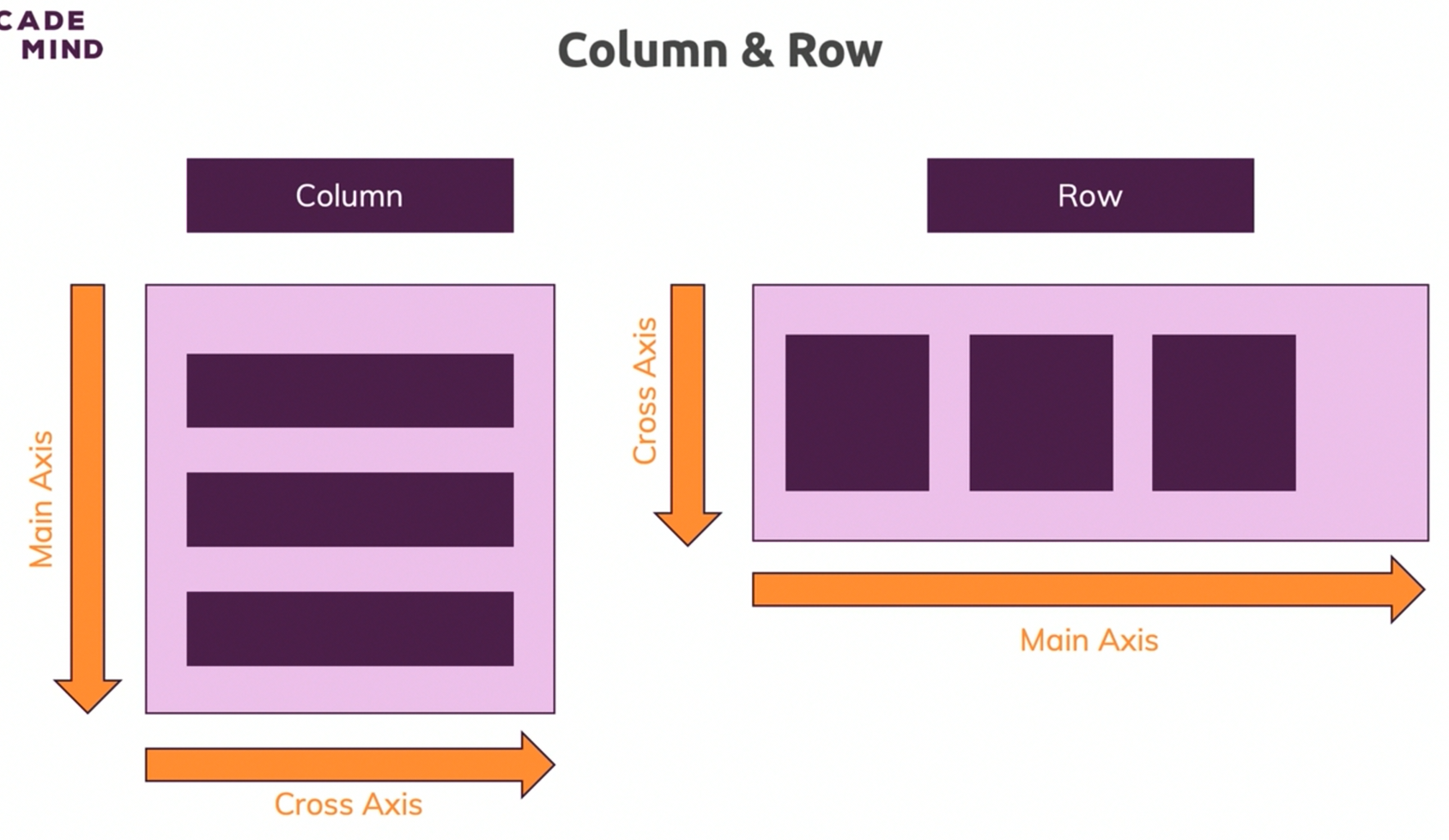
Row()Column()ListView()- …
Container() both
1.2 Button onPressed
On the first one we execute the function and pass the return value. However we should pass the pointer of the function, so that when user click the button it will call the function.
RaisedButton( child: Text('Answer 1'), onPressed: answerQuestion(), // Error here ), RaisedButton( child: Text('Answer 1'), onPressed: answerQuestion, // Fix :) ),
1.3 Anonymous Functions
onPressed: () => print('Answer 2 choosen'), //OR onPressed: () { print('Answer 2 choosen'), }
1.4 Dart list
// Creating var questions = [ 'Favorite color?', 'Favorite animal?', ]; // Accessing Text(questions.elementAt(0)), // OR Text(questions[0]),
1.5 State
State is data
Data can change
1.5.1 Stateless widget
Gets (re)rendered when input data changes
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { // ... }
1.5.2 Statefull widget
- Gets (re)rendered when input data changes or local state changes
- Everything that will effect the state, and wanted app to rerenderd will go into
setStatefunction. - Convention: naming of the classes,
..State
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget { @override State<StatefulWidget> createState() { return MyAppState(); } } class MyAppState extends State<MyApp> { var index = 0; void answerQuestion() { setState(() { index++; }); print(index); }
1.6 Class and Object Visibility in Dart
Adding leading _ (underscore) to the class name makes the class private.
- This is not a convention but a feature of the language.
final for final. StatelssWidget should be immutable, so variables inside the class should be final.
Other classes to be used need to be imported.
Convention: One widget per file
stin vscode: stateful and stateless widget snippet
1.7 Positional arguements and named arguements
Text( 'text', style: TextStyle(fontsize: 28)), textAlign: TextAlign.center, // enum
1.8 Centering widget
Conatiner ( width: double.infinity, child: ... );
1.9 Mutliple constructors
class Person { String name; int age; Person({this.name, this.age = 30}); Person.veryOld(this.name) { age = 60; } }
Instead of creating classes for one-time-use data, dart maps can be used. (Different from Java maps)
See Also: Dart Maps
1.10 Dart casting (?)
(questions[_questionIndex]['answers'] as List<String>).map(..
1.11 Dart spread(?) … operator
Adds all the values outside list, from nested lists.
1.12 Dart final vs const
final: Run time constant value. Value is unknown during developement. Can be initalized with different data.
const: Compile time constant (also (explicitly) run time constant). Value is assigned on declaration. Both variable itself or value can be const.
var dummy = const ['Hello']; dummy.add('Max'); // Doesn't work, value is const
const dummy = ['Hello']; dummy = []; // Doesn't work, dummy is constant
It's better to split larger widgets to smaller ones.
onPressed() requires void function, but we need to call with parameters:
answerQuestion() is a function.
return Answer(answerQuestion); // call by pointer // this will turn into this return Answer(() => answerQuestion(answer['score'])); // call by value
1.13 Getters
Not a function, not a value. Dart feature that allows you to assign values dynamically.
String get resultPhrase { String reusltText; if (resultScore <= 8) { resultText = 'You did it'; else if (...) { resultText = 'Something else'; } else { resultText = 'Another thing'; } return resultText; }
2 Debugging
3 Widget, Styling, Logic (Building Real App)
3.1 Most Important Widgets
3.1.1 App/Page Setup
- MaterialApp/Cupertion App
- Scaffold/CupertinoPageScaffold
3.1.2 Layout
- Container
- Row
- Column
3.1.3 Row/Column Children
- Flexible
- Expanded
3.1.4 Content Containers
- Stack (things on top of each other)
- Card
3.1.5 Repeat Elements
- ListView
- GridView
- ListTile
3.1.6 Content Types
- Text
- Image
- Icon
3.1.7 User Input
- TextField
- RaisedButton/FlatButton
- GestureDetector
- InkWell
3.2 Combining Widgets
Card(Text ()) will wrap content, since Card depends on the inside size, and Text depends on the outside size.
3.3 Populating List to Widgets
List needs to mapped to widget
transactions.map().toListtransactions.map((tx) {}).toList(map takes a function)transactions.map((tx) { return Card(child: Text(tx.title)) }).toList(returns the list of widget)More readable way of implementing;
transactions.map((tx) => Card(child: Text(tx.title))).toList;
Dart:
$varibalein strings can calltoString()function of variable
To call with dot, add curly brackets:${tx.amount}
3.4 Formatting Date
- There are no built-in easy way to format dates in flutter. For dart packages: https://pub.dev/packages.
- Third party package for formatting date-time (also localizing strings to different languages):
intl add
intl: ^0.15.8to dependencies: inpubspec.yaml. (indentation is important here, add same level withflutter:)DateFormat().format(tx.date) DateFormat('yyyy/MM/dd').format(tx.date) // with pattern DateFormat.add_yMMMd().format(tx.date) //predefined constructors for specific patterns
3.5 Text Input Widget
final amountController = TextEditingController(); TextField( decoration: InputDecoration(labelText: 'Amount'), onChanged: ..., controller: amountController, )
TextEditingController.text can give the text inside the input widget. (No need to set onChanged)
Convention:
If you have classes that are models for data, move them tolib/models.
Move widgets tolib/widget.
Dart: Consider creating a list with
final. Still you can add new itmes into list. Because only the address (pointer) of the list is final, not itself.
Don't forget: onPressed: () {} paranthesis here
Don't forget: if named arguement or positinoal arguement
3.6 Scrolling Functionality
It should be wrapped whole body. It won't work for individual elements in body.
SingleChildScrollView(...);
To apply scrolling for particular widgets, height needs to be specified in a Container().
Or for lists instead of Column() use ListView() widget. ListView() must be inside a container.
To scroll row instead of column, scrollDirection: can be used.
3.6.1 ListView.builder()
ListView(children: []) loads all the elements even they are out of the view. OK for short lists. To optimize performance for long lists use ListView.builder(), which only loads what's visible.
You must provide itemBuilder: (ctx, index) {} in ListView.builder().
ListView.builder() { itemBuilder: (ctx, index) { return Widget(... list[index] ); }, itemCount: list.length, }
3.7 Some TextField() parameters
3.7.1 Only specific type of input
- For number keyboard, in a
TextField(),keyboardType: TextInputType.number. - For allow only decimal:
TextInputType.numberWithOptions(decimal: true).
3.7.2 To submit on Enter ✔ button
onSubmitted: function(val)
or
onSubmitted: ()=> function()
Probably you want to use same function as you use on submit button.
As a convention in dart, use followed syntax (underscore as parameter) if you don't care the value that function takes;
... onSubmitted: (_) => submitData, ...
3.8 Printing double values
To print only n values after . ;
amount.toStringAsFixed(2)
This method not simply prints first 2 digits after . but rounds the value.
3.9 Adding a button to AppBar
In Scaffold()
AppBar( actions: <Widget>[ IconButton( icon: Icon(Icons.add), onPressed: ... ), ] ),
- In icon constructor, you can also custimize the apperance of icon.
3.10 Floating Button
In Scaffold();
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( child: Icon(Icons.add), ... ), floatingActionButtonLocation: FloatingActionButtonLocation.centerFloat,
3.11 Showing a Modal Bottom Sheet

showModalBottomSheet{ context: ctx, builder: (bCtx) { return Widget(...); ) } }
If you want sheet dissapper when user clicks out of the sheet (background);
showModalBottomSheet{ context: ctx, builder: (bCtx) { return GestureDetector( onTap: () {}, behaviour: HitTestBehaviour.opaque, // to not to close when user clicks white area on the widget (?) child: Widget(...); ) } }
3.11.1 Disappearing inputs on text fields, when user select another text field
It happens when the widget is stateless. Making it statefull will solve the issue.
3.12 Reaching to a field in StatefullWidget from State<>
By using widget.variable or widget.function keyword.
3.13 Automatic closing of widget when user inputs the data
Add this at the and of the function that you submit the data.
... Navigator.of(context).pop();
3.14 Themeing
In MaterialApp(),
theme: ThemeData( primarySwatch: Colors.purple, accentColor: Colors.amber, // for better matching the colors see materaial app documentation ) // ... // in another widget color: Theme.of(context).primaryColor, // since it is swatch, you can choose lighter or darker shades
primarySwatch is more complex object than primaryColor. It has material shades along with the main color.
3.15 Fonts
Add pubspec.yaml.
- For global fonts in
Materialapp;
theme: ThemeData( fontFamily: '...' )
- You can set the theme of any text to use predefined styles.
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.title
3.15.1 Editing predefined themes
In MaterialApp > theme
textTheme: ThemeData.light().textTheme.copyWith( title: TextStyle( fontFamily: 'OpenSans', fontSize: 20, ), ),
3.16 Adding Image
- Add
pubspec.yaml Image.asset('path')
3.17 SizedBox() and FractionallySizedBox()
- Container with height width or width/height factor.
- Can be used to add spacing by not specifying child.
Dart:
list.where( () {} )executes the function on every item on a list, if that function returns true, then the item is kept to returned list.
3.18 Flexible()
fit: FlexFit.tight or fit: FlexFit.loose to adding available space between widgets in a container.
- Adding
Flex()and specifyingflex:gives the available space proportionally according to flex value.
3.19 FittedBox()
Adding a text in a fitted box, will ensure the box will stay the same size, even though the text grows. In that case font size will be decrease to fit in the box.
3.19.1 Padding()
If you only use a Container to add padding then you can prefer padding widget.
3.20 Future<>
Allows to create objects which will give us a value in the future. (DatePicker, HTTP requests..)
showDatePicker( ... ).then(() {})
4 Responsive & Adapted User Interfaces and Apps
4.1 Controlling the Device Orientation
In main.dart
void main() { WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitalized(); SystemChrome.setPrefferedOrientation([ DeviceOrientation.portraitUp, DeviceOrientation.portraitDown, ]); runApp(MyApp()); }
5 Widget & Flutter Internals
5.1 Widget Tree & Element Tree
- Widget Tree: configuration (rebuilds frequently)
- Element Tree: links widgets with rendered objects (rarely rebuilds)
- Render Tree: Rendered objects on the screen (rarely rebuilds)
- If a widget refers to
MediaQueryand somehow ifMediaQuerychanges (like orientation or keyboard), thenbuild()method is called. - Rebuilding is not that bad, since its core feature of flutter and its optimized.